


Next: How to extract document
Up: Detecting Unusual Activity in
Previous: Video-prototype co-occurrence
Algorithm
If we think of the video segments as documents, and prototype features
as keywords we observe that similar problems arise in the context of
document-keyword clustering [8,4].
To illustrate the algorithm we propose, consider the following example. We took 20 departmental emails and 6 research emails
between the authors as our document set, and words which occured more then
once (across the 26 emails) as our keyword set.
Figure 5:
(a) Email-word co-occurrence matrix. (b) A reorganized
version of (a), where distinctive keywords related to research emails
are quoted. (c) Word occurrence count for corresponding words in
(b).
(d)-(f) inferred email-email similarity matrices: (d) ideal case, (e) without
feature selection, (f) with feature selection.
|
In the example we want to find the cluster of the documents (such as the
6 emails) based on the co-occurrence (figure 5(a))
information.
In the analogous video setting we seek the clusters of similar
video segments.
In figure 5(b) we show that there is an optimal
reordering of the keywords and documents (reshuffling rows and columns of
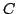 ) such that the clustering of documents and keywords can be readily
inferred from the reshuffled version of co-occurrance matrix.
We can see that the top 20 words such as ``sequence'' or ``define'' are
exclusively correlated with the first 6 emails, which are the
research emails.
To spot the 6 research emails, it is
sufficient to check for these 20 keywords, which do not occur in
other emails.
Examining the rest of matrix
) such that the clustering of documents and keywords can be readily
inferred from the reshuffled version of co-occurrance matrix.
We can see that the top 20 words such as ``sequence'' or ``define'' are
exclusively correlated with the first 6 emails, which are the
research emails.
To spot the 6 research emails, it is
sufficient to check for these 20 keywords, which do not occur in
other emails.
Examining the rest of matrix 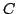 , we see that majority of the words do
not have exclusive correlation with any particular group of emails.
These include words such as ``will" or ``if", which occur with almost
every email, and words ``data" and ``people", which occur randomly.
, we see that majority of the words do
not have exclusive correlation with any particular group of emails.
These include words such as ``will" or ``if", which occur with almost
every email, and words ``data" and ``people", which occur randomly.
To cluster documents it is important to determine the informative
keywords, which might be only a small subset of the total keywords.
Such feature selection is vital in clustering the video segments as well.
Subsections



Next: How to extract document
Up: Detecting Unusual Activity in
Previous: Video-prototype co-occurrence
Mirko Visontai
2004-05-13